Organic Cotton: The Complete Guide to Sustainable Fiber Production
While conventional cotton production devastates ecosystems with toxic chemicals and consumes massive water resources, organic cotton offers a revolutionary alternative that’s transforming the textile industry. Conventional cotton is often called 'the dirtiest crop on Earth' because of its chemical-intensive farming practices and its significant global environmental impact. This sustainable approach to cotton cultivation eliminates synthetic pesticides, protects farmer health, and creates safer products for consumers worldwide.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll discover everything you need to know about organic cotton—from production methods and environmental benefits to global market trends and practical shopping guidance. Whether you’re a conscious consumer seeking healthier clothing options or a textile professional exploring sustainable sourcing, this complete resource will enhance your understanding of one of the most important developments in modern agriculture.

Introduction to Sustainable Cotton and Organic Cotton Benefits
Sustainable cotton production is at the heart of reducing the textile industry’s environmental footprint. As demand for eco-friendly products grows, organic cotton clothing has emerged as a leading choice for consumers and brands seeking to make a positive impact. Unlike conventional cotton, which relies heavily on toxic chemicals, synthetic pesticides, herbicides, and insecticides, organic cotton production is rooted in practices that protect both the environment and human health.
Organic cotton is grown without synthetic fertilizers or genetically modified seeds, ensuring that farming methods remain natural and sustainable. By embracing organic farming techniques such as crop rotation, farmers enhance biodiversity, improve soil health, and reduce the need for chemical inputs. These methods not only support healthier ecosystems but also contribute to increased crop yields and more resilient agricultural systems.
The Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) plays a crucial role in ensuring that organic cotton production meets strict environmental and social criteria. GOTS certification guarantees that every step of the process—from how the cotton is grown to how it is processed—adheres to rigorous standards, giving consumers confidence in the sustainability of their purchases.
Many brands are now shifting towards sustainable cotton production, recognizing the benefits of organic cotton for the environment and their customers. By choosing organic cotton clothing and supporting certified products, consumers and companies alike can help reduce water pollution, promote clean water, and foster a healthier planet for future generations.
What is Organic Cotton?
Organic cotton refers to cotton grown without synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, or genetically modified seeds, following strict agricultural standards that prioritize environmental health and biodiversity. Unlike conventional cotton production, which relies heavily on toxic chemicals and GMOs, organic farming creates a sustainable ecosystem that benefits both the environment and human health.
Certified organic cotton must comply with rigorous standards set by organizations like the USDA National Organic Program (NOP). These standards ensure that cotton is grown using natural pest control methods like crop rotation and beneficial insects, while maintaining soil fertility through organic matter and compost rather than synthetic fertilizers. In the United States, organic cotton plantations must meet the requirements enforced by the National Organic Program (NOP) from the USDA.
The organic certification process requires farmers to follow a specific order of regulatory steps established by certifying bodies in order to achieve organic status. Farmers must transition their land for at least three years before harvesting can be labeled organic. During this period, soil must be free from prohibited substances, and farmers must demonstrate compliance with organic farming practices. Only after meeting all requirements can cotton be labeled as organic. The transition from conventional to organic cotton requires testing to ensure no residual pesticide is present, involving a transition period of 2-3 years.
Despite its numerous benefits, organic cotton accounts for only 1-2% of global cotton production as of 2024. In fact, organic cotton uses significantly less synthetic chemicals and is often certified by labels such as GOTS or USDA Organic, providing assurance of its environmental advantages. This small percentage reflects both the challenges of converting conventional farms and the rigorous requirements necessary to maintain organic certification. However, growing consumer awareness and brand commitment to sustainability are driving increased demand and production expansion.
The fabric produced from organic cotton maintains all the natural properties that make cotton desirable—it’s breathable, comfortable, and versatile—while eliminating the chemical residues that can cause health concerns. This combination of sustainability and quality makes organic cotton an increasingly popular choice for conscious consumers seeking safer, more environmentally responsible textile options.
The Importance of Organic Cotton Production
Organic cotton production is a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture, offering significant benefits for the environment, farmers, and consumers. The Organic Trade Association highlights the vital role that certified organic cotton plays in maintaining biodiversity and supporting healthy ecosystems. By avoiding synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, organic cotton farming protects clean water sources and prevents soil degradation—problems that are widespread in conventional cotton production.
Practices such as crop rotation and composting are central to organic cotton production, enhancing soil fertility and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers. These methods not only improve the health of the land but also support thriving populations of beneficial insects and wildlife, further boosting biodiversity.
Beyond environmental benefits, organic cotton production supports fair labor practices and better working conditions for farmers. By eliminating exposure to toxic chemicals, organic farming creates safer, healthier workplaces and communities.
Consumer demand for certified organic cotton products continues to rise, with many people willing to pay a premium for items that are better for the planet and their health. According to the Textile Exchange, organic cotton production also reduces greenhouse gas emissions and promotes more efficient water use, making it a key driver of sustainability in the textile industry.
By choosing organic cotton, consumers and brands can help ensure that cotton production supports clean water, healthy soils, and vibrant ecosystems—delivering benefits that extend far beyond the farm.
Organic Cotton Production Methods
Organic cotton farming relies on time-tested natural techniques that work in harmony with nature rather than against it. These methods focus on building healthy soil ecosystems, managing pests through biological controls, and conserving water resources through efficient irrigation practices.
Crop rotation forms the foundation of organic cotton production, breaking pest cycles while naturally enriching soil fertility. Farmers typically rotate cotton with nitrogen-fixing crops like legumes, which enhance soil nutrients without synthetic fertilizers. This system supports biodiversity by creating varied habitats for beneficial insects and microorganisms that contribute to overall farm health.
Natural pest control replaces harmful insecticides with integrated pest management strategies. Farmers encourage beneficial insects that prey on cotton pests, plant companion crops that repel harmful insects, and use trap crops to divert pests away from cotton plants. These biological controls maintain ecological balance while protecting crops from damage.

Water conservation represents a critical advantage of organic cotton farming. Approximately 80% of organic cotton relies on rain-fed irrigation, significantly reducing blue water consumption compared to conventional methods. Organic farming practices like cover cropping and mulching improve soil water retention, making farms more resilient during drought periods.
Seed selection focuses exclusively on non-GMO, heritage cotton varieties that have been developed through traditional breeding methods. These seeds often demonstrate greater genetic diversity and natural resistance to local pests and diseases. Many organic farmers save seeds from their best plants, maintaining genetic diversity while adapting varieties to specific growing conditions.
Soil health management involves building organic matter through compost, crop residues, and natural amendments. Healthy soil supports robust cotton plants naturally resistant to many diseases and environmental stresses. This approach creates a self-sustaining system where soil fertility improves over time rather than depleting through chemical inputs.
Certification Standards and Requirements
The Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) represents the most comprehensive certification for organic cotton textiles, covering environmental and social criteria throughout the supply chain. GOTS certification ensures that textiles contain at least 70% organic fibers and meet strict requirements for chemical restrictions, environmental criteria, and social standards during processing. The Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) is considered the world's leading certification of organic fibers.
USDA National Organic Program (NOP) certification governs agricultural production, requiring farms to maintain detailed records, undergo annual inspections, and comply with strict regulations regarding inputs and practices. This certification covers everything from seed selection to harvesting, ensuring that cotton meets organic standards from farm to gin. USDA organic certification is a trustworthy label for cotton grown in the U.S.
The Organic Content Standard (OCS) provides verification for fabric content, tracking organic materials through the supply chain to prevent mixing with conventional cotton. OCS certification requires detailed documentation at each processing stage, ensuring traceability and preventing fraud in organic cotton markets.
OEKO-TEX STANDARD 100 offers additional chemical safety testing, verifying that finished textiles are free from harmful substances. While not specifically an organic standard, many organic cotton products also carry this certification to provide consumers with additional assurance about chemical safety and product quality.
These certification systems work together to create a comprehensive framework ensuring organic cotton products meet the highest standards for environmental sustainability, chemical safety, and social responsibility. Consumers can trust these labels to identify genuinely organic cotton products that deliver on sustainability promises. Organic cotton must meet standards set by independent certification organizations to verify its organic claims.
Environmental Benefits of Organic Cotton
Organic cotton production delivers remarkable environmental advantages compared to conventional methods, with water conservation leading the list of benefits. Studies show that organic cotton requires 91% less blue water consumption than conventionally grown cotton, primarily due to improved soil organic matter and rain-fed cultivation methods used in many organic farming regions. The production of organic cotton significantly reduces water consumption, energy usage, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Energy usage during organic cotton production averages 62% less than conventional cotton according to Textile Exchange data. This reduction stems from eliminating energy-intensive synthetic fertilizer and pesticide manufacturing, which requires significant fossil fuel inputs. Organic farming’s reliance on natural processes and renewable inputs substantially reduces the carbon footprint of cotton production.
The elimination of synthetic pesticides removes approximately 25% of global insecticide use that comes from conventional cotton farming. This reduction protects water sources from contamination, preserves beneficial insects and wildlife, and prevents the accumulation of persistent chemicals in soil and groundwater. Clean water systems benefit entire ecosystems downstream from organic cotton farms.

Biodiversity flourishes on organic cotton farms where diverse crops, beneficial insects, and soil microorganisms create balanced ecosystems. These farms often support 50% more plant and animal species than conventional operations, providing habitat for pollinators and natural pest predators that contribute to overall environmental health.
Soil conservation represents another crucial benefit, as organic farming builds soil organic matter rather than depleting it. Healthy soils sequester carbon, reduce erosion, and maintain fertility for future generations. This regenerative approach ensures that farmland remains productive long-term while contributing to climate change mitigation through carbon storage.
Comparison with Conventional Cotton Impact
Conventional cotton farming uses 10-16% of global pesticides despite occupying only 2.5% of world farmland, creating an extremely chemical-intensive agricultural system. These pesticides contaminate water supplies, harm beneficial insects, and create health risks for farmers and nearby communities through air and water pollution.
Seven of the top 15 pesticides used in conventional cotton production are classified as carcinogens by the EPA, presenting serious health risks to agricultural workers and surrounding populations. Many of these chemicals persist in the environment for years, accumulating in soil and water systems where they continue causing ecological damage.
Organic farming reduces greenhouse gas emissions by avoiding synthetic chemicals that require significant energy to manufacture and transport. Studies indicate that organic cotton production generates 46% fewer CO2 emissions than conventional methods, contributing to climate change mitigation while producing the same end product.
Water contamination from conventional cotton farming affects millions of people worldwide, particularly in developing countries where environmental regulations may be less stringent. Pesticide runoff creates dead zones in water bodies, kills fish and aquatic life, and makes water unsafe for human consumption or irrigation of food crops.
The contrast becomes clear when comparing input requirements: conventional cotton may require 20-25 pesticide applications per growing season, while organic cotton uses zero synthetic chemicals. This difference translates to measurably cleaner air, water, and soil in regions where organic cotton is grown.
Health and Quality Benefits
Organic cotton eliminates pesticide residues that commonly cause skin irritation and allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Conventional cotton processing leaves chemical traces in finished textiles, which can trigger dermatitis, respiratory issues, and other health problems for people with chemical sensitivities or compromised immune systems. The use of synthetic pesticides in conventional cotton can trigger skin irritation and allergies in humans.
The hypoallergenic properties of organic cotton make it particularly suitable for individuals with sensitive skin, eczema, or multiple chemical sensitivity. Without toxic chemical treatments, organic cotton allows skin to breathe naturally while reducing exposure to substances that can exacerbate existing health conditions or create new sensitivities. Consumers with skin sensitivities often prefer organic cotton garments because they are hypoallergenic.
Natural fiber strength remains intact in organic cotton because harsh chemical processing is avoided during production. Conventional cotton often undergoes aggressive chemical treatments that can weaken fibers and reduce fabric durability. Organic cotton clothes typically last longer and maintain their softness and quality through repeated washing and wear. Easy care is another advantage—simply machine wash organic cotton garments in cold or warm water with mild detergent, and tumble dry on low to help preserve their quality and extend their lifespan. For best results, pretreat stains on organic cotton by gently applying a mild stain remover before washing, which helps maintain the fabric’s appearance and durability.

Children and infants particularly benefit from organic cotton products because their developing systems are more vulnerable to chemical exposure. Organic cotton clothing and bedding provide a safer environment for growing children while offering the same comfort and practicality parents expect from cotton textiles.
The absence of synthetic chemicals in organic cotton makes it safer for people who work in textile manufacturing facilities. Workers handling organic cotton experience fewer respiratory problems, skin conditions, and other occupational health issues compared to those processing conventionally grown cotton with chemical residues.
Organic cotton products often feel softer and more comfortable against the skin because natural cotton fibers retain their inherent properties without chemical modification. Many users report that organic cotton clothing becomes increasingly comfortable with each wash, developing a pleasant texture that synthetic treatments cannot replicate.
To keep your garments in the best condition, consider keeping a file of care instructions for your organic cotton clothing to easily reference the best maintenance practices.
Global Organic Cotton Production
India leads global organic cotton production with 51% of the world’s supply, leveraging its large agricultural sector and growing environmental awareness among farmers. Indian organic cotton farms often employ traditional farming knowledge combined with modern organic techniques, creating successful models for sustainable cotton agriculture that support rural communities. India is the largest producer of organic cotton, followed by China and Turkey.
China produces 19% of global organic cotton, focusing on meeting domestic demand for sustainable textiles while serving international markets. Chinese organic cotton production has grown significantly as environmental concerns increase and government policies encourage sustainable agricultural practices across the country.
Turkey contributes 7% of world organic cotton production, with Kyrgyzstan also producing 7% of the global total. These countries have developed specialized organic cotton sectors that serve European markets demanding sustainable textile materials. Their geographic location provides advantages for efficient export to major consumer markets.
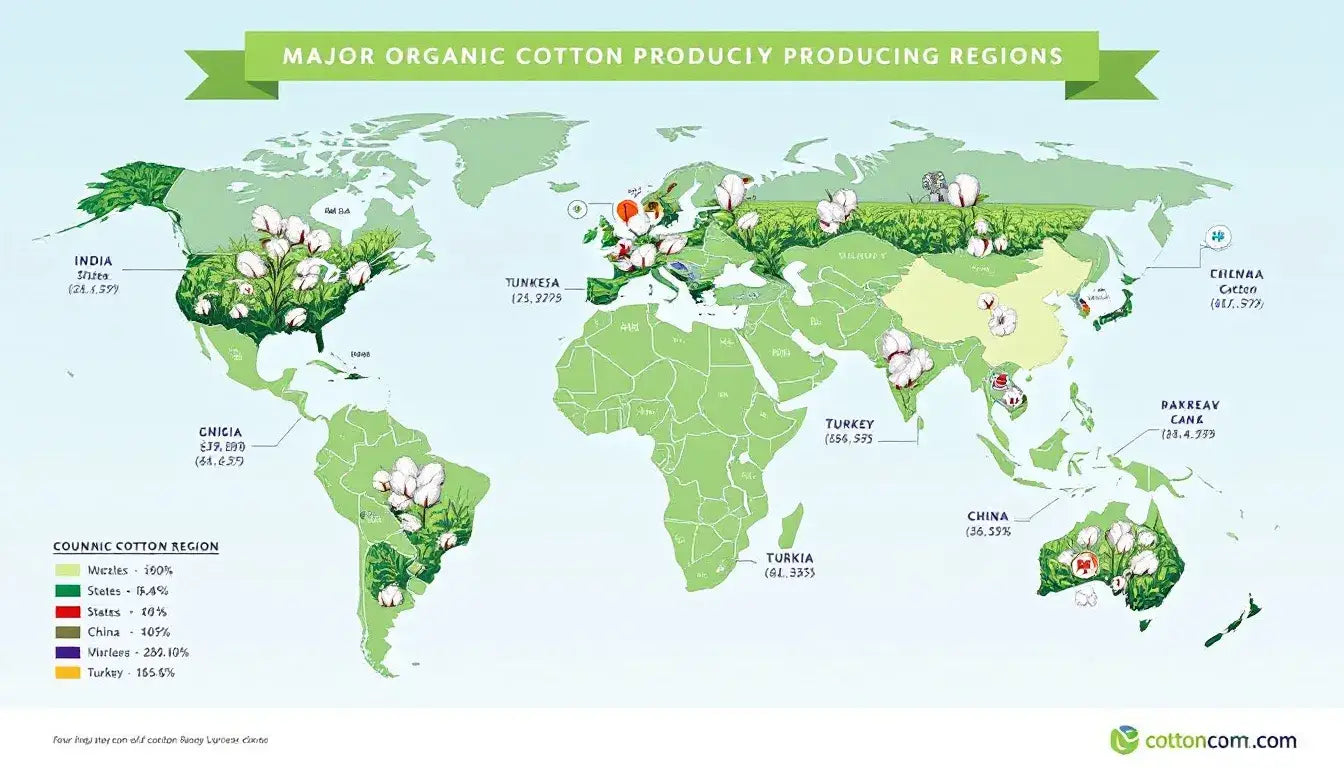
Egypt’s SEKEM initiative pioneered organic cotton cultivation since 1990, demonstrating remarkable results by reducing pesticide use by 90% while maintaining profitable operations. This success story proves that organic cotton farming can be both environmentally beneficial and economically viable, inspiring similar projects across Africa and the Middle East.
African countries produce organic cotton in at least eight nations, with growing support from international development organizations and fair trade initiatives. These programs help small-scale farmers transition to organic methods while providing market access and premium prices that improve rural livelihoods.
The geographic distribution of organic cotton production reflects both climatic advantages and market demand factors. Many organic cotton farms are located in regions with suitable rainfall patterns, reducing irrigation requirements while producing high-quality fiber that meets international organic standards.
Industry Support and Market Growth
Major brands including Nike, Walmart, and C&A have committed to supporting organic cotton supply chains through long-term purchasing agreements and farmer education programs. These partnerships provide market stability for organic cotton farmers while helping brands meet sustainability goals and consumer demands for environmentally responsible products.
Textile Exchange reports steadily increasing demand from the fashion industry, with many brands setting targets to source significant percentages of their cotton from organic sources. In response, a growing proportion of organic cotton products are now being sold by major brands and retailers, reflecting their commitment to sustainability and quality standards. This market growth is driven by consumer awareness of environmental issues and brand recognition that sustainability creates competitive advantages.
Fair trade initiatives complement organic certification by ensuring farmers receive fair prices for their cotton while supporting community development projects. These programs address social sustainability alongside environmental benefits, creating comprehensive approaches to responsible cotton production that benefit all stakeholders.
The market for organic cotton continues expanding as consumers become more aware of the environmental and health impacts of conventional cotton production. Growing demand from developed countries creates opportunities for farmers in developing nations to improve their livelihoods through organic cotton cultivation.
Industry support includes technical assistance programs that help farmers transition to organic methods and achieve certification. These initiatives provide training, financial support, and market connections that make organic cotton farming accessible to smallholder farmers who might otherwise lack resources for conversion.
Supporting Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture is essential for preserving ecosystem health and promoting biodiversity, and organic cotton production is a leading example of these principles in action. Through organic farming practices such as crop rotation, composting, and natural pest control, farmers can maintain fertile soils and reduce their reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
Conventional cotton production often leads to soil degradation and water pollution due to the heavy use of synthetic fertilizers and chemical pesticides. In contrast, organic cotton farming enhances soil fertility, supports higher crop yields, and minimizes environmental harm. By nurturing the land with organic methods, farmers create more resilient agricultural systems that benefit both people and nature.
Many farmers are embracing sustainable agriculture by transitioning to organic cotton production, improving their livelihoods while reducing their environmental impact. Consumers play a crucial role in this movement by choosing certified organic cotton products and advocating for eco-friendly farming practices.
The benefits of sustainable agriculture are clear: improved crop yields, reduced water pollution, and enhanced biodiversity. By supporting organic cotton production, we can help create a healthier environment, promote fair and equitable farming practices, and ensure that future generations enjoy the many advantages of sustainable agriculture.
Organic Cotton Products and Applications
Organic cotton clothing represents the largest market segment, encompassing everything from basic t-shirts and jeans to high-end fashion garments. Many brands now offer complete clothing lines made from certified organic cotton, providing consumers with safer alternatives that don’t compromise on style, comfort, or durability.
Home textiles including bedding, towels, curtains, and upholstery increasingly feature organic cotton as consumers recognize the benefits of reducing chemical exposure in their living spaces. Organic cotton bedding offers particularly appealing benefits for people who spend significant time in close contact with fabrics during sleep.
Baby products represent a crucial application area where parents prioritize safety and seek organic cotton clothing and bedding for infants. The gentle, chemical-free nature of organic cotton makes it ideal for babies’ sensitive skin while providing the breathability and comfort that cotton is known for.

Medical textiles utilize organic cotton for bandages, surgical supplies, and hospital linens where purity and safety are paramount. Healthcare facilities increasingly choose organic cotton products to reduce patient exposure to chemicals while maintaining the absorbency and sterility required for medical applications.
Specialty products like organic cotton towels, bathrobes, and spa accessories appeal to consumers seeking luxury items that align with their environmental values. These products often command premium prices while delivering superior comfort and peace of mind regarding chemical exposure.
The versatility of organic cotton allows its use in virtually any application where conventional cotton is used, from industrial applications to high-fashion garments. This flexibility makes organic cotton an excellent substitute that doesn’t require compromise on functionality or aesthetic appeal.
How to Identify Genuine Organic Cotton
Looking for GOTS certification labels on finished textile products provides the most reliable method for identifying authentic organic cotton. GOTS labels indicate that products contain at least 70% organic fibers and meet strict environmental and social standards throughout the manufacturing process, ensuring comprehensive sustainability.
Verifying USDA Organic certification for raw cotton materials offers additional assurance, particularly for products that may not carry GOTS certification. This certification appears on labels and product descriptions, confirming that cotton was grown according to organic agricultural standards without synthetic chemicals or GMOs.
Checking for Organic Content Standard (OCS) verification helps confirm organic fiber content in textiles, particularly useful when shopping for products that may blend organic cotton with other materials. OCS certification tracks organic content through the supply chain, preventing dilution with conventional materials.

Avoiding products with vague “natural” or “eco-friendly” claims without proper certification protects consumers from greenwashing. Many products use misleading marketing language without meeting organic standards, so insisting on recognized certification ensures that purchases truly support sustainable cotton production.
Reading product labels carefully reveals important details about cotton sourcing and processing. Genuine organic cotton products typically provide detailed information about certifications, manufacturing locations, and sustainable practices, while uncertified products often use vague or incomplete descriptions.
Shopping from reputable brands and retailers with transparent sustainability policies increases the likelihood of finding authentic organic cotton products. Many responsible companies provide detailed information about their supply chains, certifications, and environmental commitments, making it easier for consumers to make informed choices.
Understanding the difference between organic cotton and other sustainable cotton initiatives helps consumers make appropriate choices. While programs like Better Cotton Initiative support improved conventional farming, only certified organic cotton eliminates synthetic chemicals entirely and meets the strictest environmental standards. To learn more about sustainability initiatives, organic farming practices, or our company's eco-friendly commitments, visit our additional resources or dedicated sections.
Comparing prices can also provide clues about authenticity, as genuine organic cotton typically costs more due to higher production costs and certification requirements. Products priced similarly to conventional cotton may not be authentic organic, though sales and bulk purchasing can sometimes reduce price differences.
Organic cotton represents far more than just another textile option—it embodies a fundamental shift toward sustainable agriculture that benefits farmers, consumers, and the planet. The dramatic reduction in water usage, elimination of toxic chemicals, and protection of biodiversity demonstrate that responsible production methods can create products that are both environmentally sound and commercially viable.
As consumer awareness grows and more brands commit to sustainable sourcing, organic cotton production will continue expanding to meet increasing demand. This market growth creates opportunities for farmers worldwide to adopt healthier growing methods while providing consumers with safer, higher-quality products that align with their values.
The choice to support organic cotton through conscious purchasing decisions creates ripple effects throughout the textile industry, encouraging more farmers to transition to organic methods and more brands to prioritize sustainability. Every organic cotton purchase represents a vote for cleaner water, healthier soil, and safer working conditions for agricultural communities worldwide.
Take action today by looking for certified organic cotton labels when shopping for clothes, bedding, and other textile products. Your commitment to supporting organic cotton production helps create a more sustainable future while ensuring that you and your family enjoy the many benefits of chemical-free, naturally grown cotton products.
Conclusion
In conclusion, organic cotton production represents a vital step toward sustainable agriculture and a reduced environmental impact for the textile industry. Certified organic cotton is grown without synthetic pesticides, synthetic fertilizers, or genetically modified seeds, making it a healthier and more responsible choice for both consumers and the environment. Organic cotton is biodegradable, unlike many conventional textiles.
The benefits of organic cotton production are far-reaching: reduced chemical use, water conservation, improved soil health, and support for fair labor practices. As many brands shift toward sustainable cotton production, consumers have the power to drive this positive change by choosing certified organic cotton products and supporting responsible brands.
By promoting organic cotton production and sustainable agriculture, we can create a healthier environment, support farmers, and ensure a more sustainable future for the textile industry and the planet. The importance of organic cotton production cannot be overstated—it is essential that we continue to support and advocate for sustainable agriculture practices.
As consumers, our choices matter. By making informed decisions and demanding more sustainable, eco-friendly products, we can help create a better future for the textile industry, the environment, and generations to come.

Materials & Fabrics for Clothing Production
Explore cotton, French terry, jersey, fleece, and sustainable blends used in premium apparel manufacturing.
Explore Premium Apparel Fabrics Guide
Printing Techniques for Apparel Production
Screen printing, embroidery, puff prints, and digital methods for custom clothing manufacturing.
Explore Custom Apparel Printing Techniques
Dyeing Techniques in Clothing Manufacturing
Garment dye, pigment, acid wash, and stone wash finishes that create unique apparel designs.
Compare Apparel Finishing Techniques
Popular Clothing Items for Custom Apparel
Hoodies, joggers, t-shirts, leggings, and biker shorts — essentials for every apparel collection.
Explore Popular Custom Clothing Items
Trends & Designs in Modern Apparel
Oversized fits, streetwear influences, and activewear styles driving custom clothing production.
Explore Trends & Designs for Apparel Development
Sustainable & Ethical Clothing Production
OEKO-TEX® certified fabrics, organic cotton, and ethical apparel manufacturing in Portugal.
Understand Sustainable & Ethical Clothing Production
Essentials for Custom Clothing Production
Custom labels, packaging, and trims that elevate your apparel brand in production.
Explore Essentials for Custom Clothing Production
Resources for Custom Clothing Production
Startup guides, logistics support, and scaling strategies for apparel brands and wholesale clients.
Explore Resources for Custom Clothing Production
Clothing Manufacturing Glossary
Explore a complete glossary of clothing and garment manufacturing terms
The Complete Clothing Manufacturing Glossary
The Best Clothing Manufacturers
Explore global clothing manufacturers by country
Explore The Best Clothing Manufacturers
The Latest Clothing Industry Updates in 2025
Discover the latest news about important topics in the clothing industry in 2025,
Stay On Top Of Clothing Industry Updates
Worldwide Best Manufacturers of Clothes in 2026
Top clothing manufacturers worldwide organized by product type
Find The Worldwide Best Manufacturers of Clothes